In July 2024, Rongxing Li's team from the College of Surveying and Geo-Informatics at Tongji University, in collaboration with Researcher Xiangbin Cui from the Polar Research Institute of China and Associate Professor Shengkai Zhang from the Chinese Antarctic Surveying and Mapping Research Center, successfully published an article titled "The Current Status and Trends of Stability Monitoring for the Three Major Antarctic Ice Shelves" in both Chinese and English editions of Science China: Earth Sciences. The study systematically analyzed the instability and long-term temporal changes of the three major Antarctic ice shelves. It comprehensively examined key parameters, including surface elevation, basal melting, surface meltwater, crevasses, suture zones, calving fronts, grounding lines, ice flow velocity, and mass balance changes of the three ice shelves. The detailed statistical results are shown in the table below.
Table 1 Parameters for the three largest ice shelves and the reference ice shelf in Antarctica
Parameters |
RIS |
FRIS |
AIS |
LBIS |
PIIS |
TIS |
Elevation changes (m yr-1) |
-0.03±0.09 (1995-2020) |
-0.06±0.08 (1995-2020) |
0.01±0.04 (1995-2020) |
-0.34±1.2 (1963-2001) |
-2.30±0.38 (1994-2012) |
0.20±0.75 (1994-2012) |
Basal melting (m yr-1) |
0.4±0.3 (1994-2018) |
0.2±0.3 (1994-2018) |
0.8±0.7 (1994-2018) |
2.2±2.3 (1994-2018) |
14.0±1.6 (1994-2018) |
11.5±2.0 (1994-2018) |
Surface meltwater (km2) |
9.65 (0%) (2017-01) |
2.72 (0%) (2017-01) |
1031.38 (2%) (2017-01) |
138.71 (14%) (1990-2000) |
6.54 (0%) (2017-01) |
0.00 (0%) (2017-01) |
Major rifts propagation rate (km yr-1) |
2.43±0.05 (1975-2017) |
2.77±0.00 (2005-2019) |
1.53±0.13 (2002-2019) |
/ |
8.18±0.04 (2015-2017) |
1.23±0.04 (2002-2014) |
Lateral shift of suture zones (m) |
33±77 (2003-2014) |
39±82 (2003-2014) |
67±98 (2003-2014) |
/ |
/ |
/ |
Ice front area change rate inside the PSI boundary (km2 yr-1) |
-337±28 (0%) (1963-2021) |
37±15 (0%) (1963-2021) |
0±0 (0%) (1963-2021) |
/ |
-883±127 (-13%) (1973-2021) |
-98±100 (-2%) (1963-2021) |
In addition, the study selected the collapsed Larsen B Ice Shelf, the rapidly changing and structurally altered Pine Island Ice Shelf, and the accelerating Totten Ice Shelf as reference ice shelves. A comparative analysis of the key parameters between the three major Antarctic ice shelves and the reference ice shelves was conducted to determine the change status and stability trends of the three major ice shelves. The results showed that the variations in multiple key parameters of the three major ice shelves were relatively minor compared to those of the reference ice shelves.
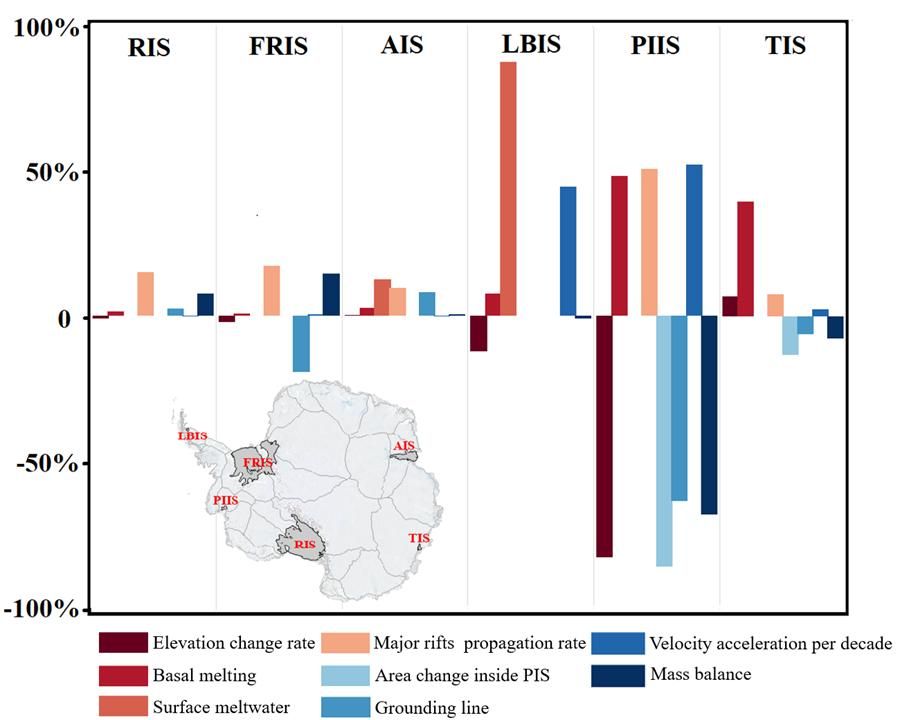
Figure 1 Histogram of parameters for the three largest ice shelves and the reference ice shelves in Antarctica
At present, the three major ice shelves are in a stable state of natural variation, and no significant structural changes are expected in the short term. However, under the context of global climate warming, there is considerable uncertainty in this trend, necessitating long-term monitoring to assess its potential impact on global sea level rise.
| 